Create StatefulSet¶
This page describes how to create a StatefulSet through image and YAML files.
StatefulSet is a common resource in Kubernetes, and Deployment, mainly used to manage the deployment and scaling of Pod collections. The main difference between the two is that Deployment is stateless and does not save data, while StatefulSet is stateful and is mainly used to manage stateful applications. In addition, Pods in a StatefulSet have a persistent ID, which makes it easy to identify the proper Pod when matching storage volumes.
Through the container management module of AI platform, workloads on multicloud and multiclusters can be easily managed based on proper role permissions, including the creation of StatefulSets, update, delete, elastic scaling, restart, version rollback and other full life cycle management.
Prerequisites¶
Before using image to create StatefulSets, the following prerequisites need to be met:
-
In the Container Management module Integrate Kubernetes Cluster or Create Kubernetes Cluster, and can access the cluster UI interface.
-
The current operating user should have NS Editor or higher permissions, for details, refer to Namespace Authorization.
-
When there are multiple containers in a single instance, make sure that the ports used by the containers do not conflict, otherwise the deployment will fail.
Create by image¶
Follow the steps below to create a statefulSet using image.
-
Click Clusters on the left navigation bar, then click the name of the target cluster to enter Cluster Details.
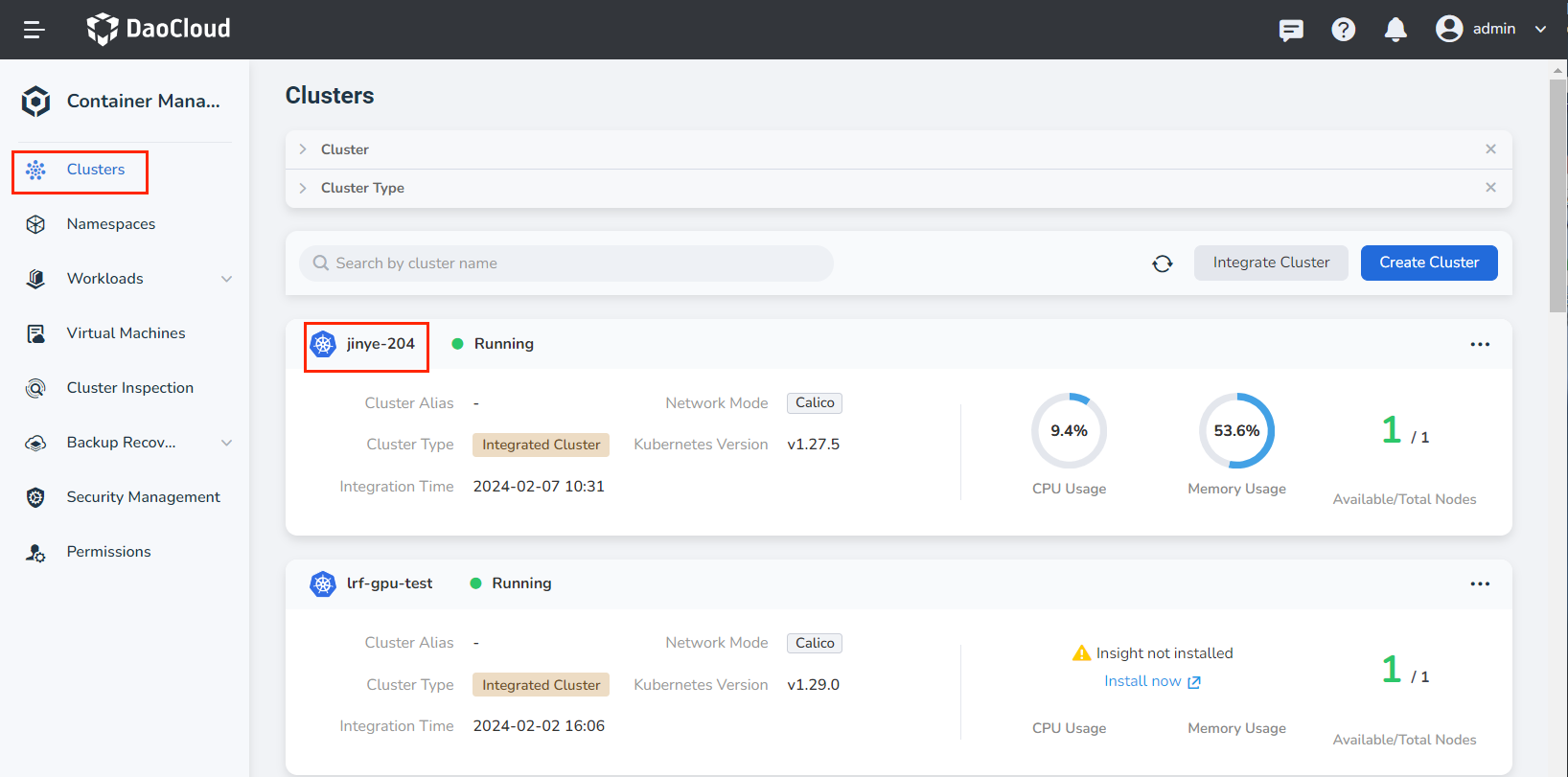
-
Click Workloads -> StatefulSets in the left navigation bar, and then click the Create by Image button in the upper right corner.
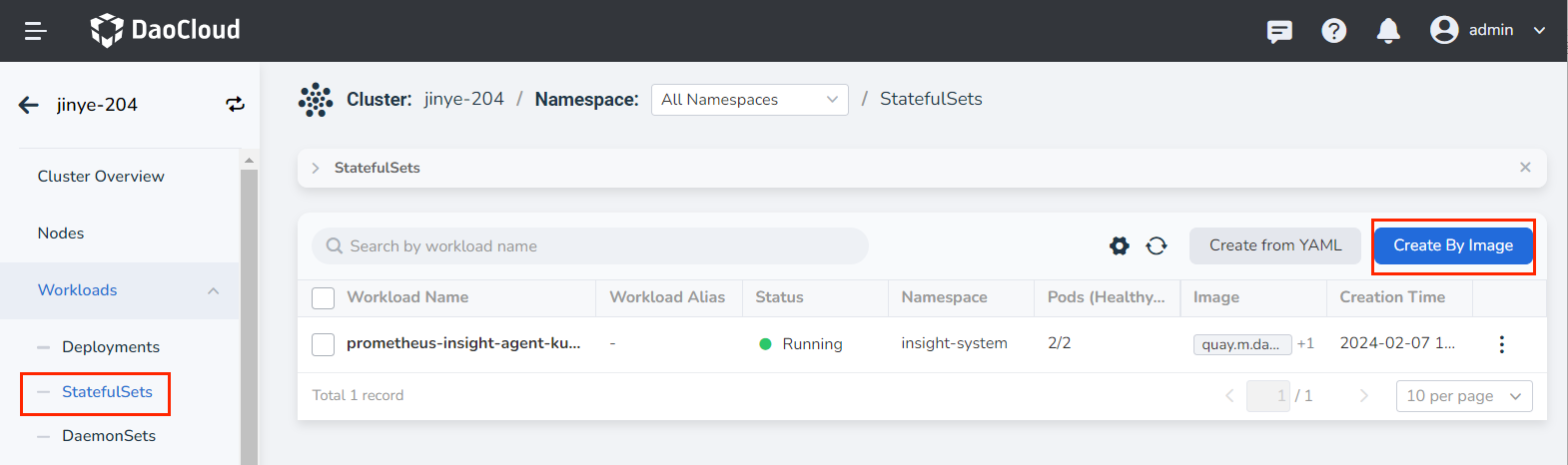
-
Fill in Basic Information, Container Settings, Service Settings, Advanced Settings, click OK in the lower right corner of the page to complete the creation.
The system will automatically return to the list of StatefulSets , and wait for the status of the workload to become running . If the workload status is abnormal, refer to Workload Status for specific exception information.
Click ┇ on the right side of the New Workload column to perform operations such as update, delete, elastic scaling, restart, and version rollback on the workload.
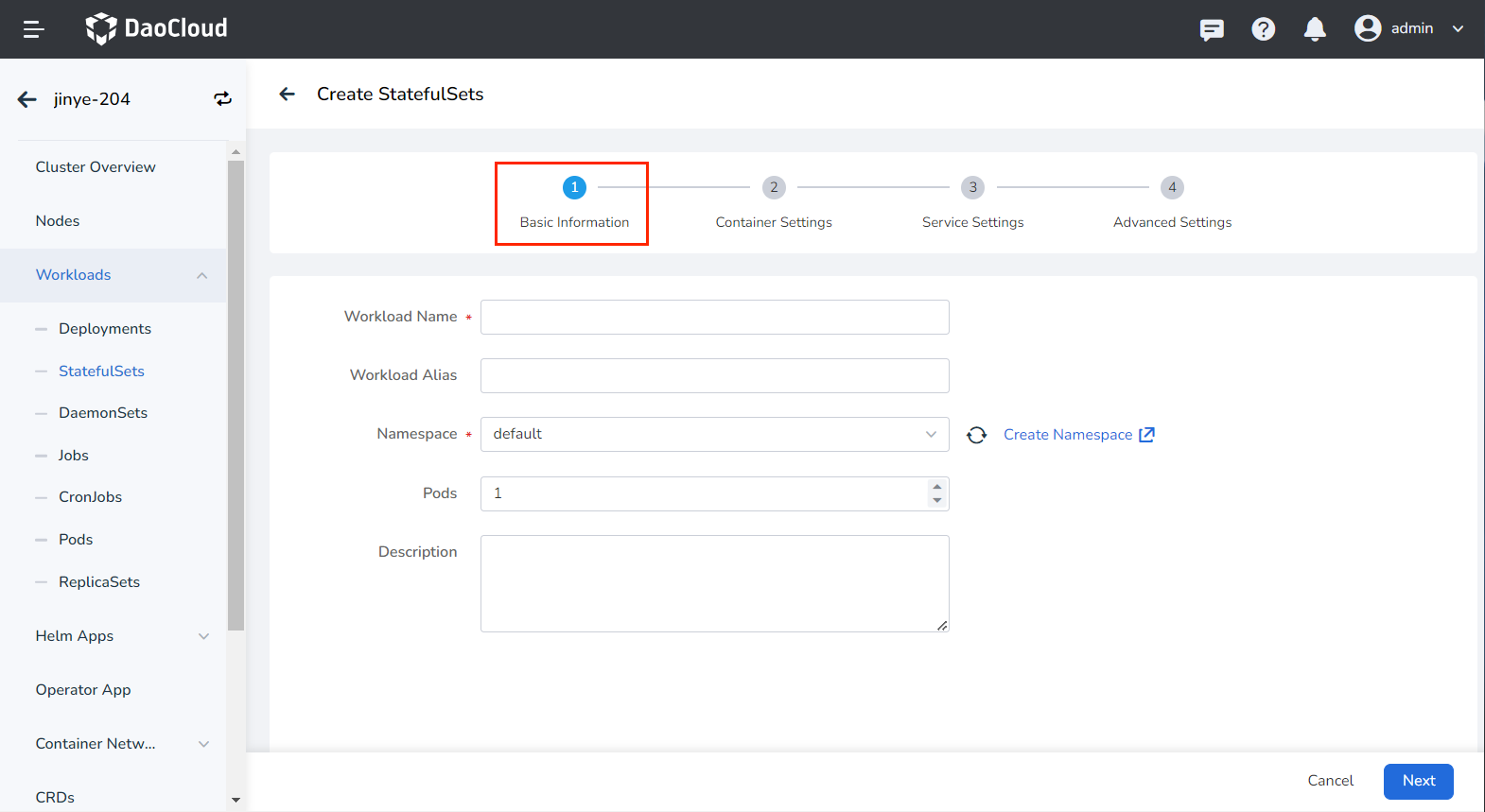
Basic Information¶
- Workload Name: can contain up to 63 characters, can only contain lowercase letters, numbers, and a separator ("-"), and must start and end with a lowercase letter or number, such as deployment-01. The name of the same type of workload in the same namespace cannot be repeated, and the name of the workload cannot be changed after the workload is created.
- Namespace: Select the namespace where the newly created payload will be deployed. The default namespace is used by default. If you can't find the desired namespace, you can go to Create a new namespace according to the prompt on the page.
- Pods: Enter the number of Pod instances for the load, and one Pod instance is created by default.
- Description: Enter the description information of the payload and customize the content. The number of characters cannot exceed 512.
Container settings¶
Container setting is divided into six parts: basic information, life cycle, health check, environment variables, data storage, and security settings. Click the tab below to view the requirements of each part.
Container settings is only configured for a single container. To add multiple containers to a pod, click + on the right to add multiple containers.
When configuring container-related parameters, you must correctly fill in the container name and image parameters, otherwise you will not be able to proceed to the next step. After filling in the settings with reference to the following requirements, click OK .
- Container Name: Up to 63 characters, lowercase letters, numbers and separators ("-") are supported. Must start and end with a lowercase letter or number, eg nginx-01.
- Image: Enter the address or name of the image. When entering the image name, the image will be pulled from the official DockerHub by default.
- Image Pull Policy: After checking Always pull image , the image will be pulled from the registry every time the workload restarts/upgrades. If it is not checked, only the local image will be pulled, and only when the image does not exist locally, it will be re-pulled from the container registry. For more details, refer to Image Pull Policy.
- Privileged container: By default, the container cannot access any device on the host. After enabling the privileged container, the container can access all devices on the host and enjoy all the permissions of the running process on the host.
- CPU/Memory Quota: Requested value (minimum resource to be used) and limit value (maximum resource allowed to be used) of CPU/Memory resource. Please configure resources for containers as needed to avoid resource waste and system failures caused by excessive container resources. The default value is shown in the figure.
- GPU Exclusive: Configure the GPU usage for the container, only positive integers are supported. The GPU quota setting supports setting exclusive use of the entire GPU or part of the vGPU for the container. For example, for an 8-core GPU, enter the number 8 to let the container exclusively use the entire length of the card, and enter the number 1 to configure a 1-core vGPU for the container.
Before setting exclusive GPU, the administrator needs to install the GPU and driver plug-in on the cluster nodes in advance, and enable the GPU feature in Cluster Settings.
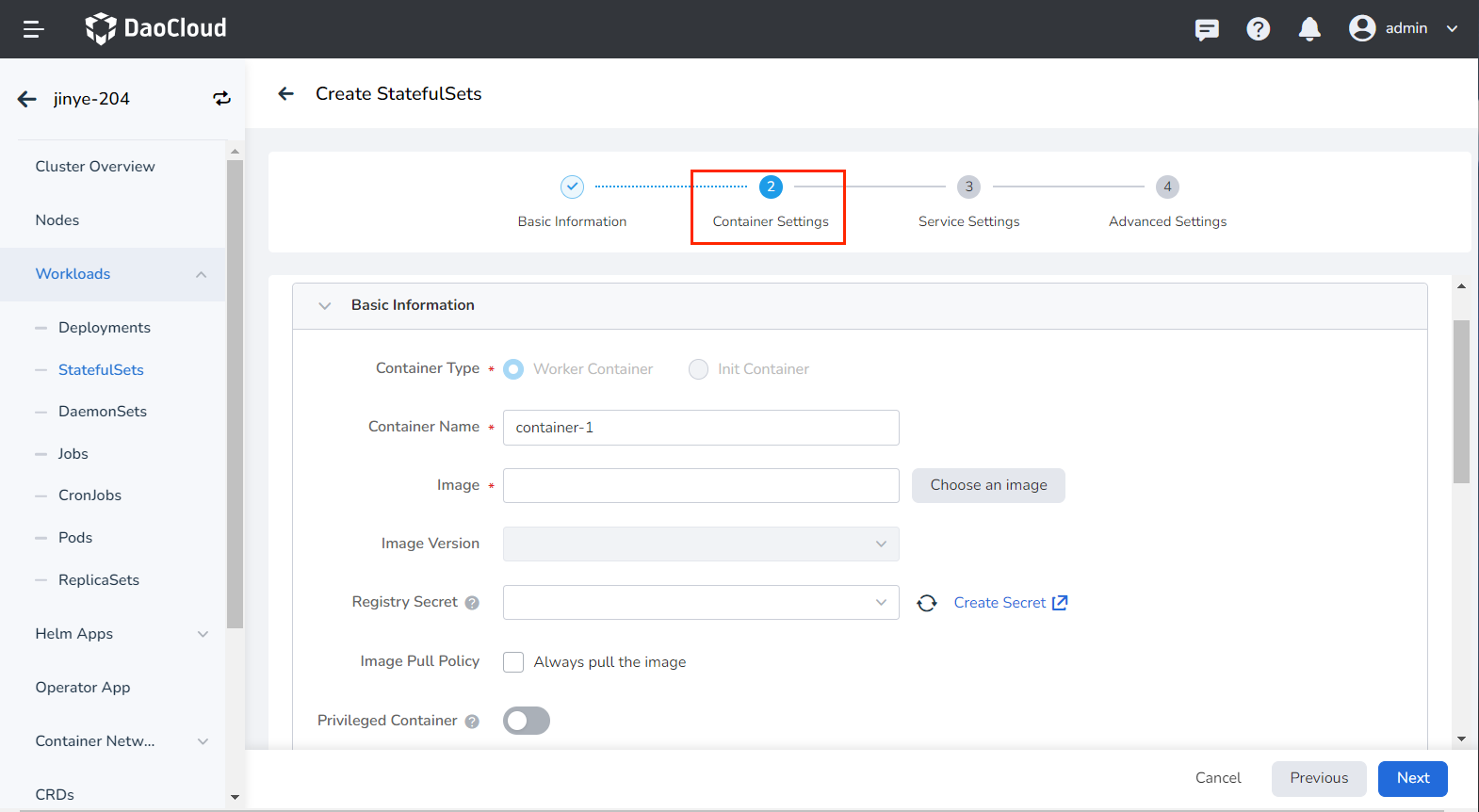
Set the commands that need to be executed when the container starts, after starting, and before stopping. For details, refer to Container Lifecycle Configuration.
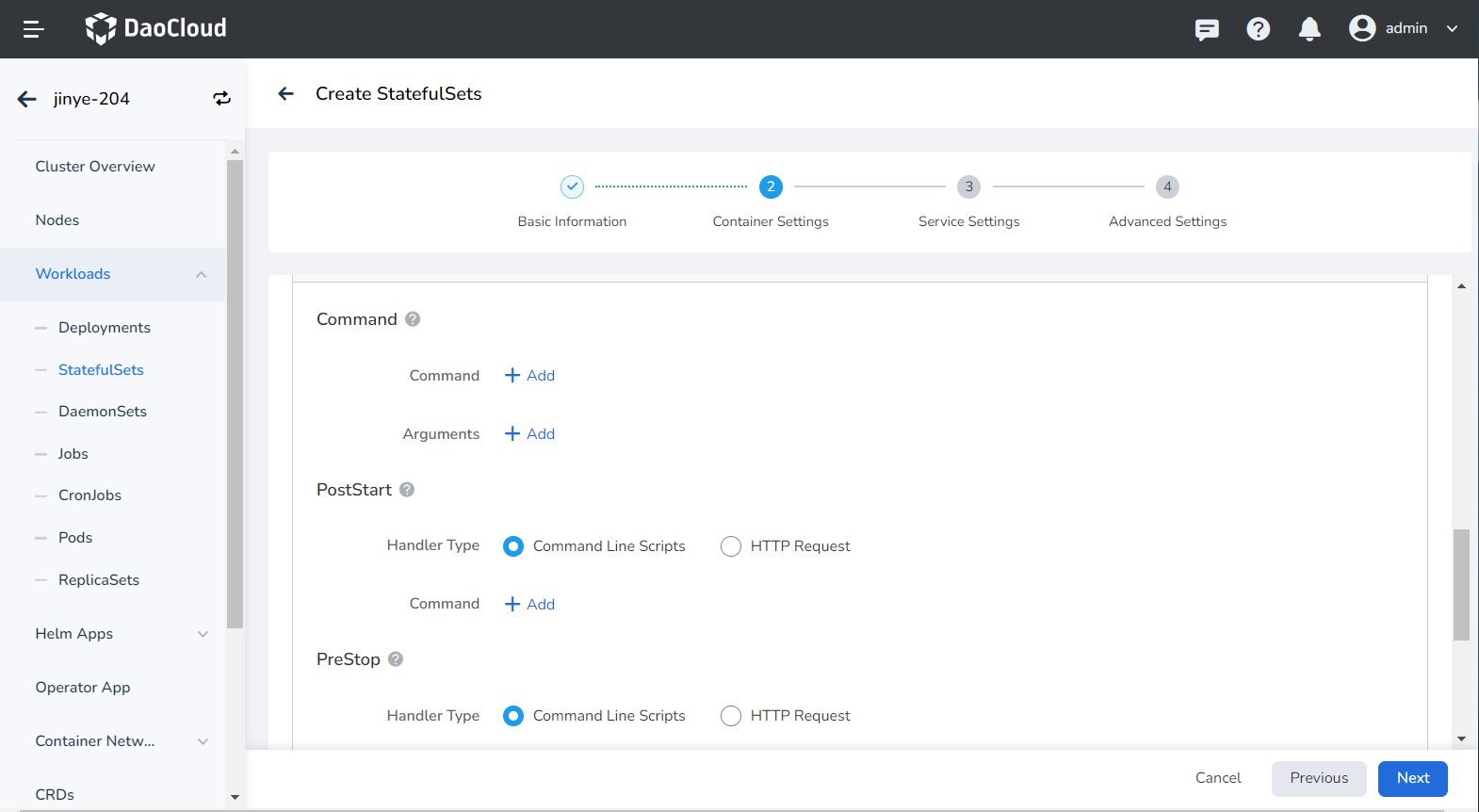
Used to judge the health status of containers and applications. Helps improve app usability. For details, refer to Container Health Check Configuration.
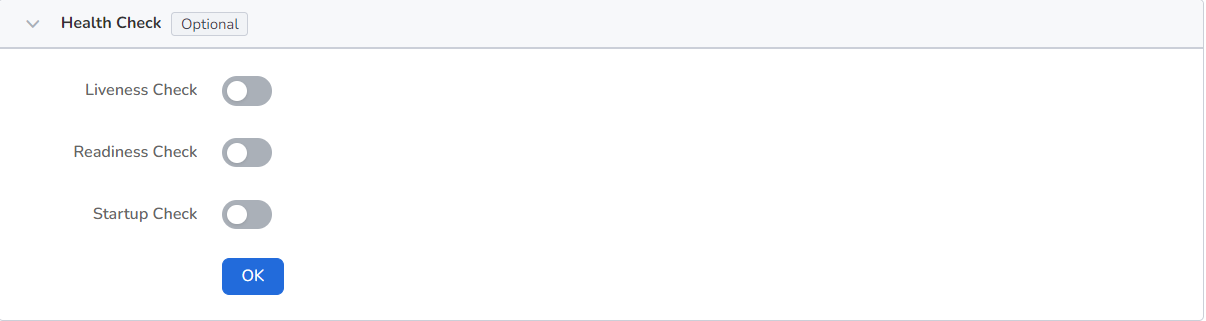
Configure container parameters within the Pod, add environment variables or pass settings to the Pod, etc. For details, refer to Container environment variable settings.
Configure the settings for container mounting volumes and data persistence. For details, refer to Container Data Storage Configuration.
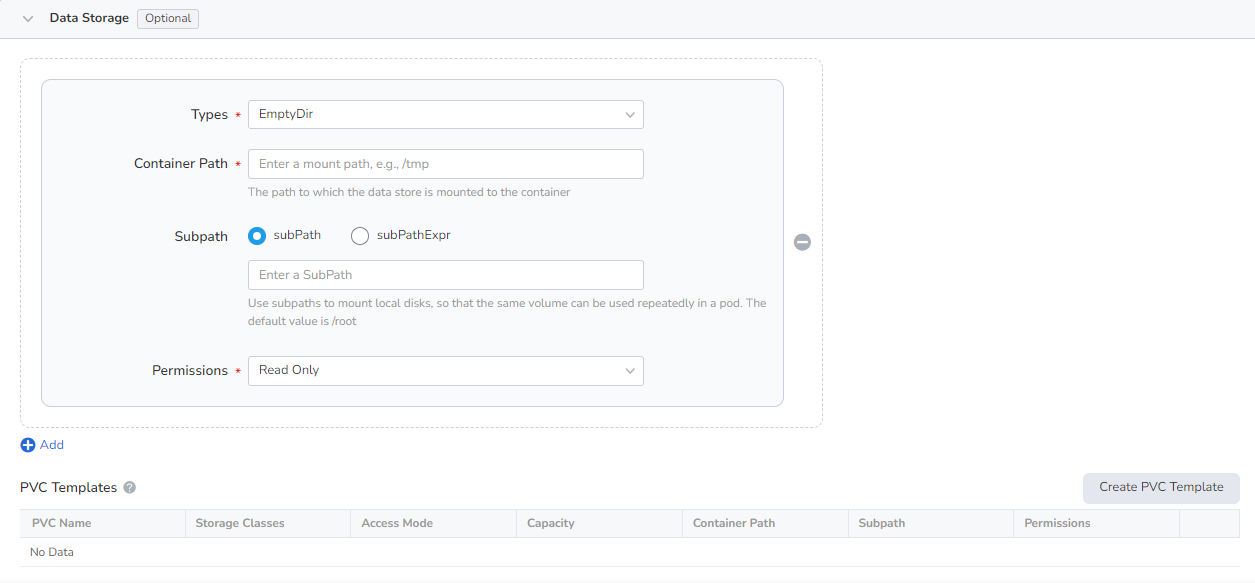
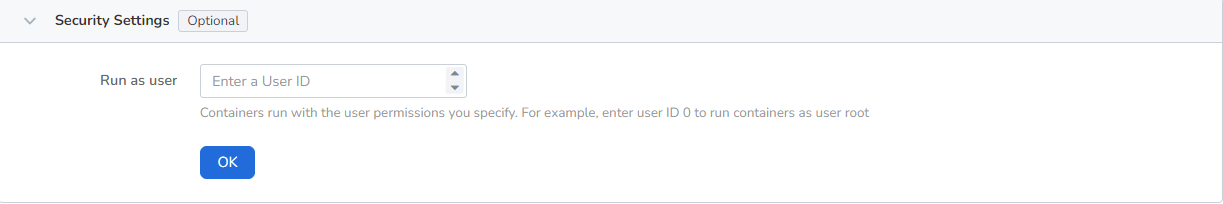
Containers are securely isolated through Linux's built-in account authority isolation mechanism. You can limit container permissions by using account UIDs (digital identity tokens) with different permissions. For example, enter 0 to use the privileges of the root account.
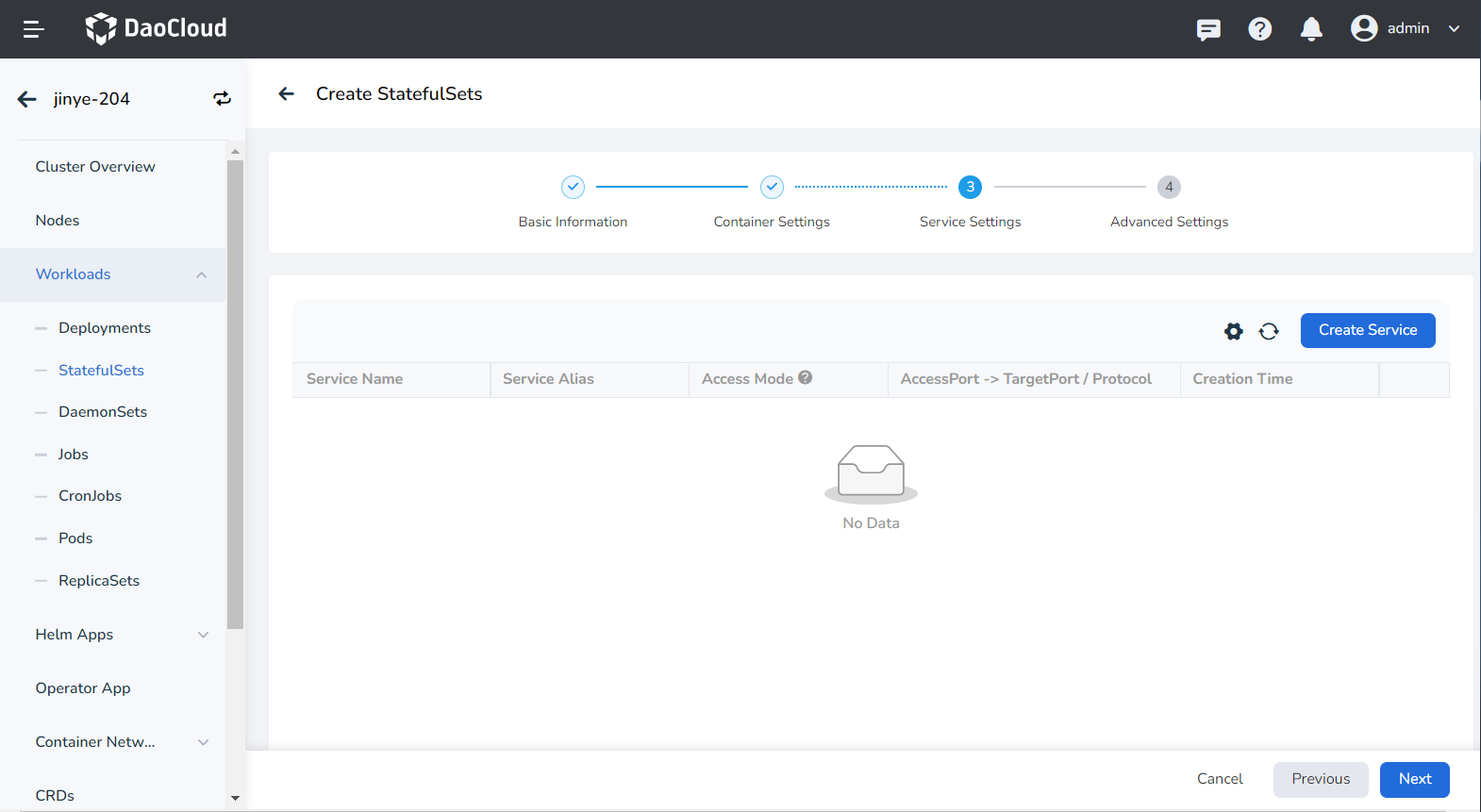
Service settings¶
Configure Service (Service) for the statefulset, so that the statefulset can be accessed externally.
-
Click the Create Service button.
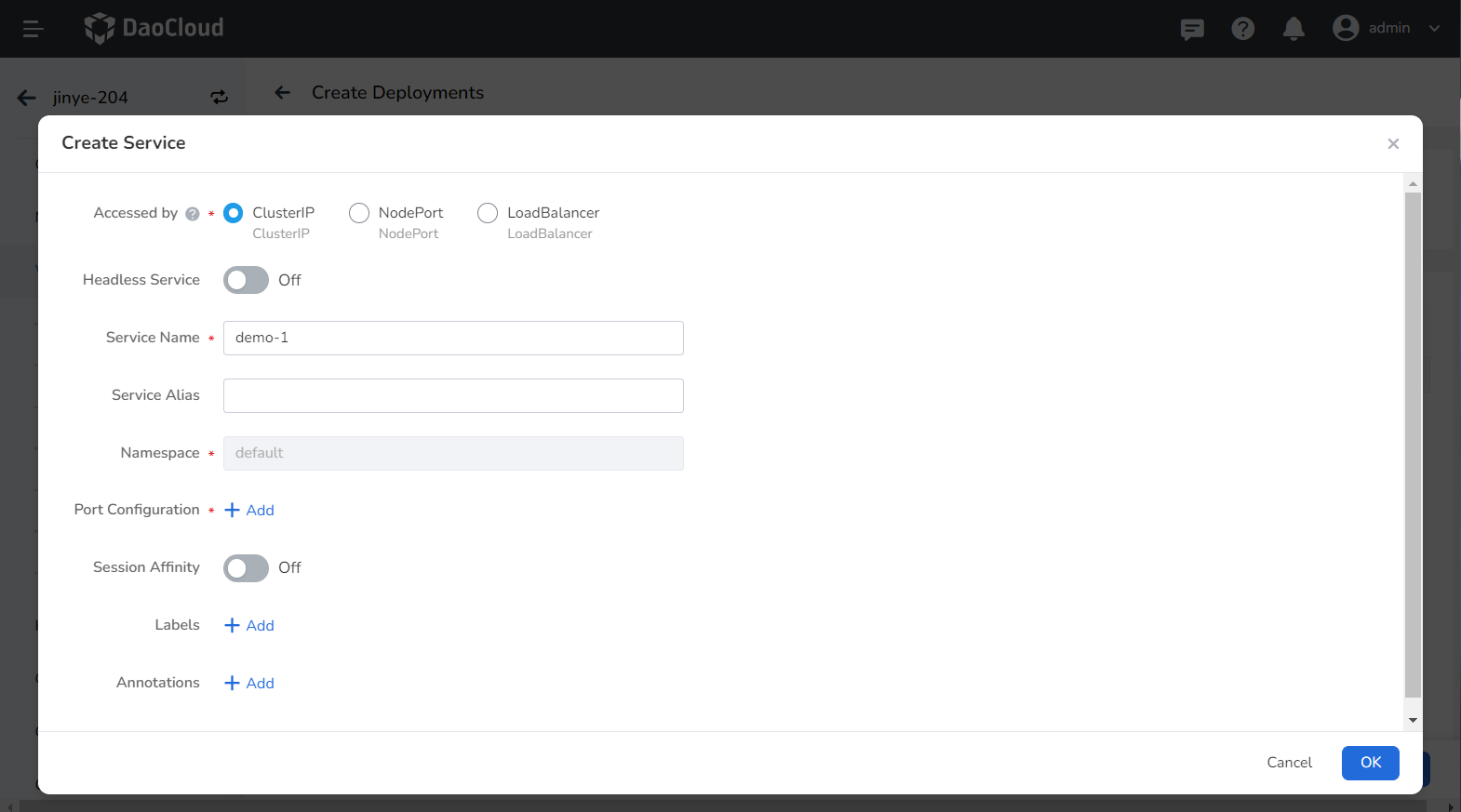
-
Refer to Create Service to configure service parameters.
-
Click OK and click Next .
Advanced settings¶
Advanced setting includes four parts: load network settings, upgrade policy, scheduling policy, label and annotation. You can click the tabs below to view the requirements of each part.
- For container NIC settings, refer to Workload Usage IP Pool
- DNS settings
In some cases, the application will have redundant DNS queries. Kubernetes provides DNS-related settings options for applications, which can effectively reduce redundant DNS queries and increase business concurrency in certain cases.
-
DNS Policy
- Default: Make the container use the domain name resolution file pointed to by the --resolv-conf parameter of kubelet. This setting can only resolve external domain names registered on the Internet, but cannot resolve cluster internal domain names, and there is no invalid DNS query.
- ClusterFirstWithHostNet: The domain name file of the application docking host.
- ClusterFirst: application docking with Kube-DNS/CoreDNS.
- None: New option value introduced in Kubernetes v1.9 (Beta in v1.10). After setting to None, dnsConfig must be set. At this time, the domain name resolution file of the container will be completely generated through the settings of dnsConfig.
-
Nameservers: fill in the address of the domain name server, such as 10.6.175.20 .
- Search domains: DNS search domain list for domain name query. When specified, the provided search domain list will be merged into the search field of the domain name resolution file generated based on dnsPolicy, and duplicate domain names will be deleted. Kubernetes allows up to 6 search domains.
- Options: Configuration options for DNS, where each object can have a name attribute (required) and a value attribute (optional). The content in this field will be merged into the options field of the domain name resolution file generated based on dnsPolicy. If some options of dnsConfig options conflict with the options of the domain name resolution file generated based on dnsPolicy, they will be overwritten by dnsConfig.
- Host Alias: the alias set for the host.
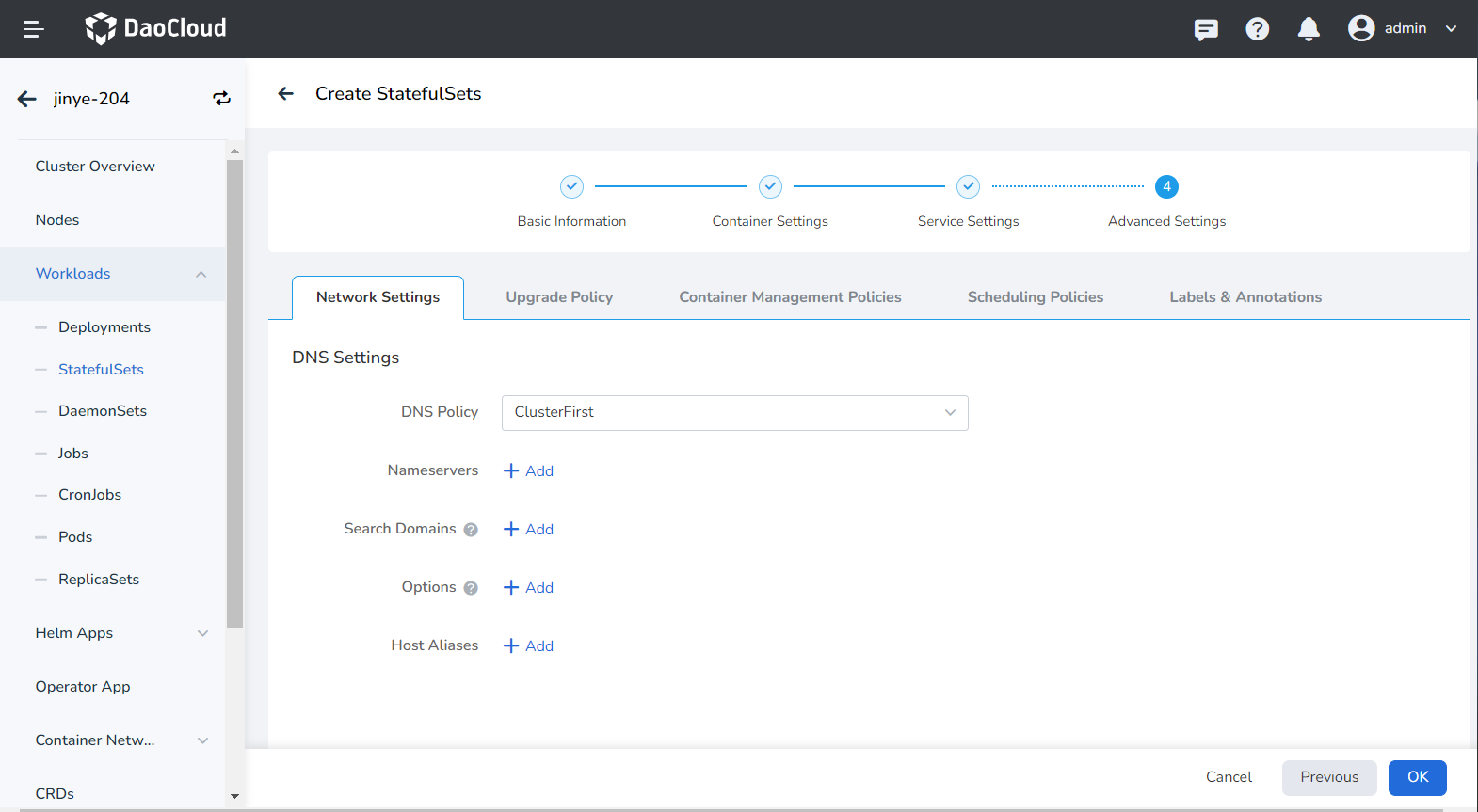
- Upgrade Mode: Rolling upgrade refers to gradually replacing instances of the old version with instances of the new version. During the upgrade process, business traffic will be load-balanced to the old and new instances at the same time, so the business will not be interrupted. Rebuild and upgrade refers to deleting the workload instance of the old version first, and then installing the specified new version. During the upgrade process, the business will be interrupted.
- Revision History Limit: Set the number of old versions retained when the version is rolled back. The default is 10.
- Graceful Period: The execution period (0-9,999 seconds) of the command before the workload stops, the default is 30 seconds.
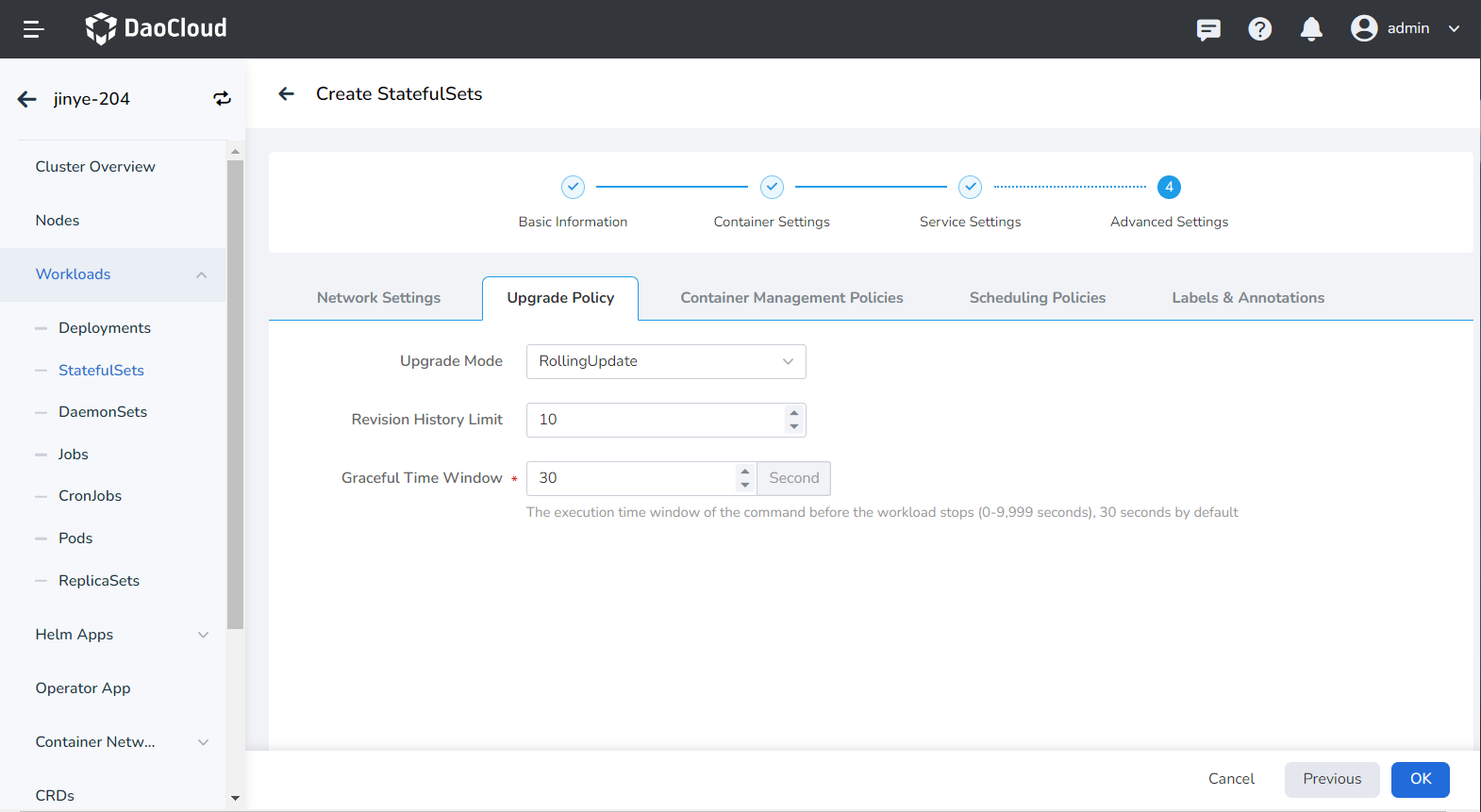
Kubernetes v1.7 and later versions can set Pod management policies through .spec.podManagementPolicy , which supports the following two methods:
-
OrderedReady : The default Pod management policy, which means that Pods are deployed in order. Only after the deployment of the previous Pod is successfully completed, the statefulset will start to deploy the next Pod. Pods are deleted in reverse order, with the last created being deleted first.
-
Parallel : Create or delete containers in parallel, just like Pods of the Deployment type. The StatefulSet controller starts or terminates all containers in parallel. There is no need to wait for a Pod to enter the Running and ready state or to stop completely before starting or terminating other Pods. This option only affects the behavior of scaling operations, not the order of updates.
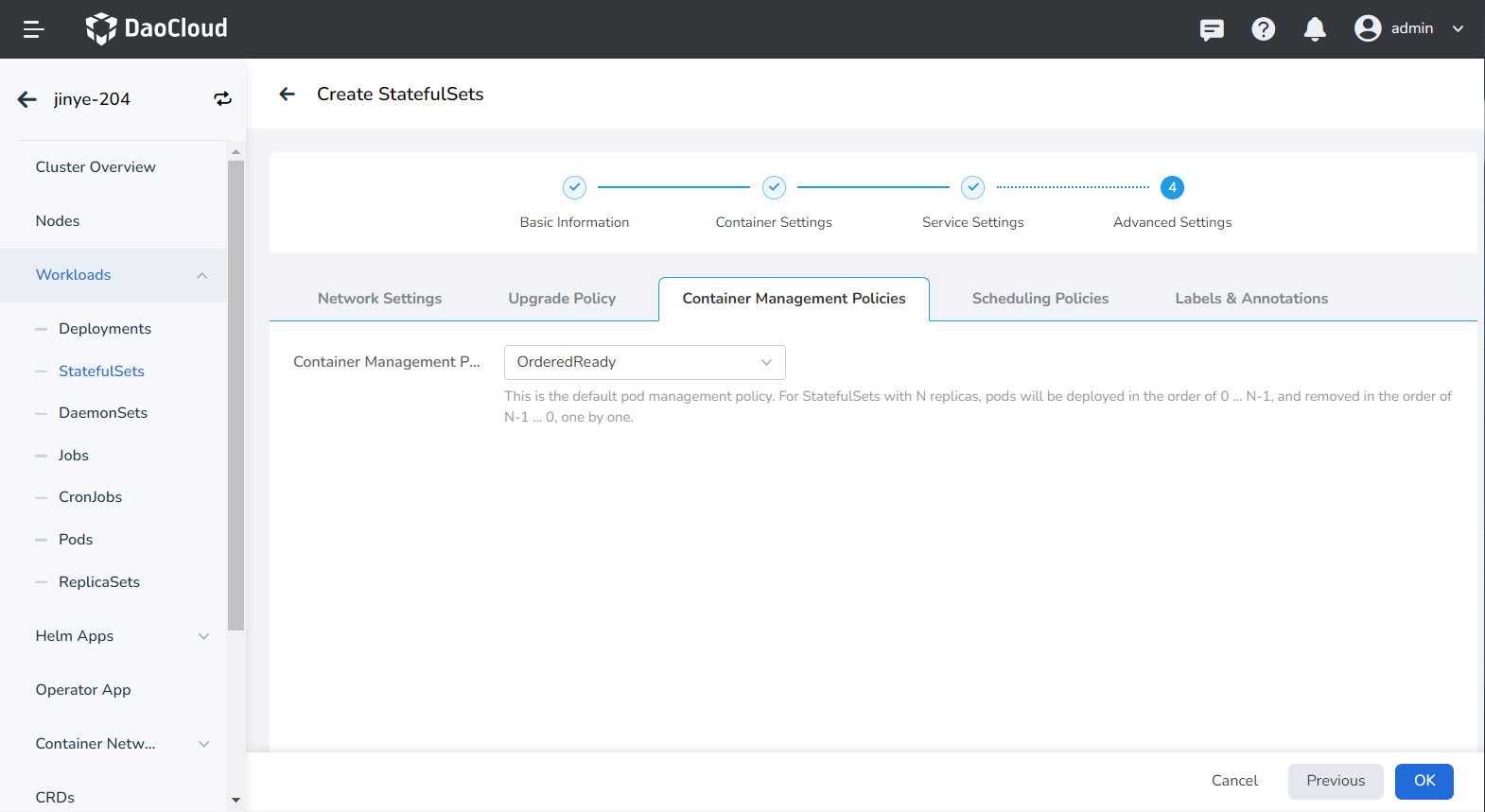
- Tolerance time: When the node where the workload instance is located is unavailable, the time for rescheduling the workload instance to other available nodes, the default is 300 seconds.
- Node affinity: According to the label on the node, constrain which nodes the Pod can be scheduled on.
- Workload Affinity: Constrains which nodes a Pod can be scheduled to based on the labels of the Pods already running on the node.
- Workload anti-affinity: Constrains which nodes a Pod cannot be scheduled to based on the labels of Pods already running on the node.
- Topology domain: namely topologyKey, used to specify a group of nodes that can be scheduled. For example, kubernetes.io/os indicates that as long as the node of an operating system meets the conditions of labelSelector, it can be scheduled to the node.
For details, refer to Scheduling Policy.
You can click the Add button to add tags and annotations to workloads and pods.
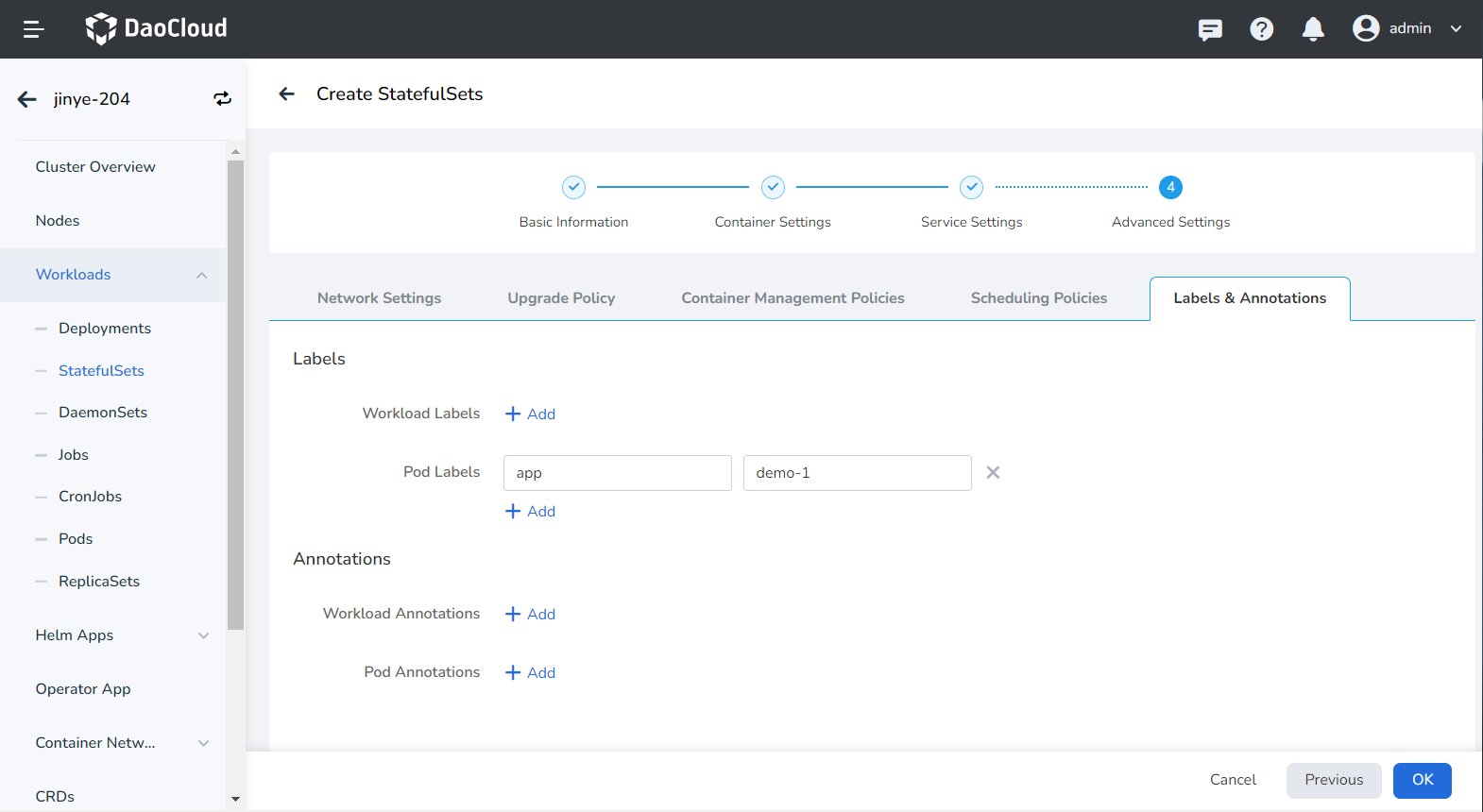
Create from YAML¶
In addition to image, you can also create statefulsets more quickly through YAML files.
-
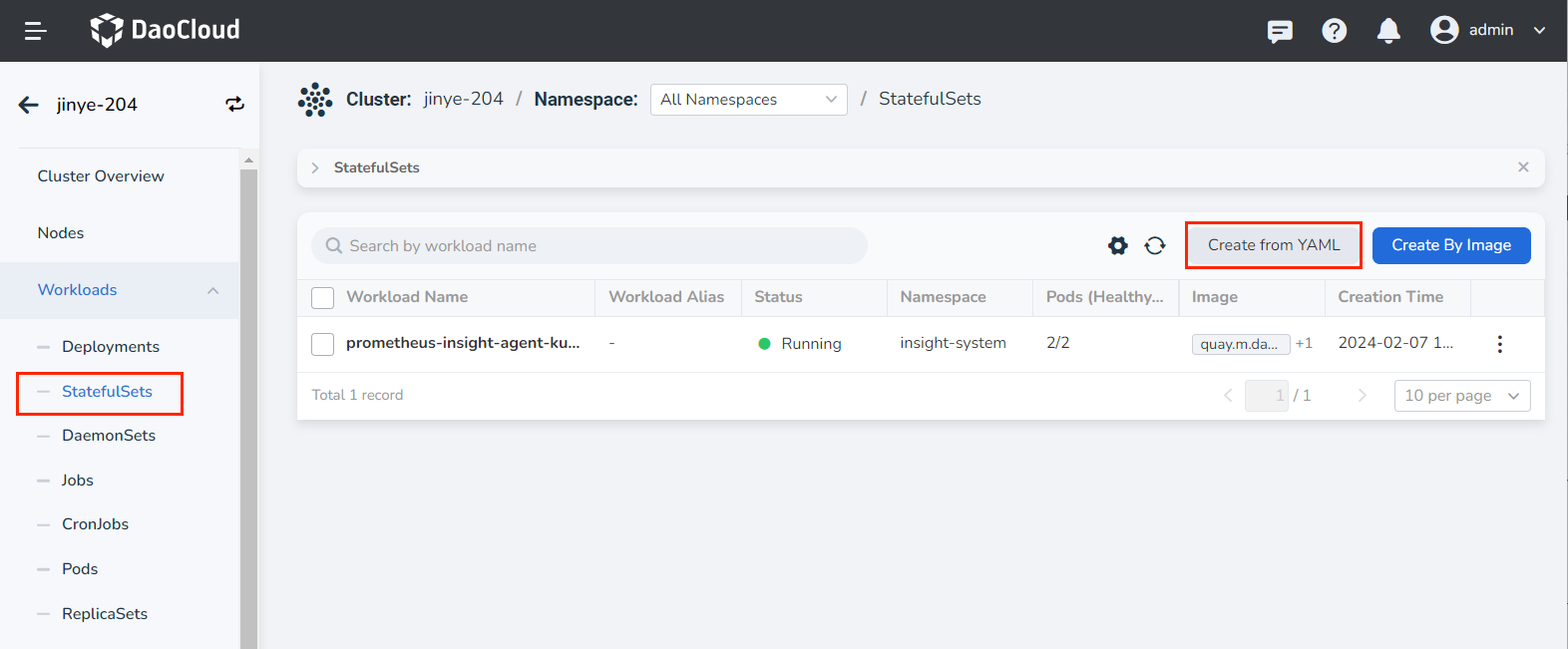
Click Clusters on the left navigation bar, and then click the name of the target cluster to enter the Cluster Details page.

-
On the cluster details page, click Workloads -> StatefulSets in the left navigation bar, and then click the Create from YAML button in the upper right corner of the page.
-
Enter or paste the YAML file prepared in advance, click OK to complete the creation.
Click to see an example YAML for creating a statefulSet
kind: StatefulSet
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql
namespace: default
uid: d3f45527-a0ab-4b22-9013-5842a06f4e0e
resourceVersion: '20504385'
generation: 1
creationTimestamp: '2022-09-22T09:34:10Z'
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: mysql.presslabs.org/v1alpha1
kind: MysqlCluster
name: test-mysql-123
uid: 5e877cc3-5167-49da-904e-820940cf1a6d
controller: true
blockOwnerDeletion: true
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: mysql.presslabs.org
app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql
mysql.presslabs.org/cluster: test-mysql-123
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: test-mysql-123
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: mysql.presslabs.org
app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql
app.kubernetes.io/version: 5.7.31
mysql.presslabs.org/cluster: test-mysql-123
annotations:
config_rev: '13941099'
prometheus.io/port: '9125'
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
secret_rev: '13941101'
spec:
volumes:
-name: conf
emptyDir: {}
- name: init-scripts
emptyDir: {}
- name: config-map
configMap:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql
defaultMode: 420
- name: data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: data
initContainers:
-name: init
image: docker.m.daocloud.io/bitpoke/mysql-operator-sidecar-5.7:v0.6.1
args:
- clone-and-init
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql-operated
env:
- name: MY_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: MY_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: MY_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: MY_SERVICE_NAME
value: mysql
- name: MY_CLUSTER_NAME
value: test-mysql-123
- name: MY_FQDN
value: $(MY_POD_NAME).$(MY_SERVICE_NAME).$(MY_NAMESPACE)
- name: MY_MYSQL_VERSION
value: 5.7.31
- name: BACKUP_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql-operated
key: BACKUP_USER
optional: true
- name: BACKUP_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql-operated
key: BACKUP_PASSWORD
optional: true
resources: {}
volumeMounts:
- name: conf
mountPath: /etc/mysql
- name: config-map
mountPath: /mnt/conf
- name: data
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
containers:
- name: mysql
image: docker.m.daocloud.io/mysql:5.7.31
ports:
- name: mysql
containerPort: 3306
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: MY_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: MY_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: MY_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: MY_SERVICE_NAME
value: mysql
- name: MY_CLUSTER_NAME
value: test-mysql-123
- name: MY_FQDN
value: $(MY_POD_NAME).$(MY_SERVICE_NAME).$(MY_NAMESPACE)
- name: MY_MYSQL_VERSION
value: 5.7.31
- name: ORCH_CLUSTER_ALIAS
value: test-mysql-123.default
- name: ORCH_HTTP_API
value: http://mysql-operator.mcamel-system/api
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-secret
key: ROOT_PASSWORD
optional: false
- name: MYSQL_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-secret
key: USER
optional: true
- name: MYSQL_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-secret
key: PASSWORD
optional: true
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-secret
key: DATABASE
optional: true
resources:
limits:
cpu: '1'
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 512Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: conf
mountPath: /etc/mysql
- name: data
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- mysqladmin
- '--defaults-file=/etc/mysql/client.conf'
- ping
initialDelaySeconds: 60
timeoutSeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/sh
- '-c'
- >-
test $(mysql --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/client.conf -NB -e
'SELECT COUNT(*) FROM sys_operator.status WHERE
name="configured" AND value="1"') -eq 1
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 2
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
lifecycle:preStop:
exec:
command:
- bash
- /etc/mysql/pre-shutdown-ha.sh
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
- name: sidecar
image: docker.m.daocloud.io/bitpoke/mysql-operator-sidecar-5.7:v0.6.1
args:
- config-and-serve
ports:
- name: sidecar-http
containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql-operated
env:
- name: MY_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: MY_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: MY_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: MY_SERVICE_NAME
value: mysql
- name: MY_CLUSTER_NAME
value: test-mysql-123
- name: MY_FQDN
value: $(MY_POD_NAME).$(MY_SERVICE_NAME).$(MY_NAMESPACE)
- name: MY_MYSQL_VERSION
value: 5.7.31
- name: XTRABACKUP_TARGET_DIR
value: /tmp/xtrabackup_backupfiles/
resources:
limits:
cpu: '1'
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 64Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: conf
mountPath: /etc/mysql
- name: data
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 8080
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
- name: metrics-exporter
image: prom/mysqld-exporter:v0.13.0
args:
- '--web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9125'
- '--web.telemetry-path=/metrics'
- '--collect.heartbeat'
- '--collect.heartbeat.database=sys_operator'
ports:
- name: prometheus
containerPort: 9125
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: MY_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: MY_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: MY_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: MY_SERVICE_NAME
value: mysql
- name: MY_CLUSTER_NAME
value: test-mysql-123
- name: MY_FQDN
value: $(MY_POD_NAME).$(MY_SERVICE_NAME).$(MY_NAMESPACE)
- name: MY_MYSQL_VERSION
value: 5.7.31
- name: USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql-operated
key: METRICS_EXPORTER_USER
optional: false
- name: PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: test-mysql-123-mysql-operated
key: METRICS_EXPORTER_PASSWORD
optional: false
- name: DATA_SOURCE_NAME
value: $(USER):$(PASSWORD)@(127.0.0.1:3306)/
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /metrics
port: 9125
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 30
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
- name: pt-heartbeat
image: docker.m.daocloud.io/bitpoke/mysql-operator-sidecar-5.7:v0.6.1
args:
- pt-heartbeat
- '--update'
- '--replace'
- '--check-read-only'
- '--create-table'
- '--database'
- sys_operator
- '--table'
- heartbeat
- '--utc'
- '--defaults-file'
- /etc/mysql/heartbeat.conf
- '--fail-successive-errors=20'
env:
- name: MY_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: MY_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: MY_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: MY_SERVICE_NAME
value: mysql
- name: MY_CLUSTER_NAME
value: test-mysql-123
- name: MY_FQDN
value: $(MY_POD_NAME).$(MY_SERVICE_NAME).$(MY_NAMESPACE)
- name: MY_MYSQL_VERSION
value: 5.7.31
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 64Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: conf
mountPath: /etc/mysql
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
securityContext:
runAsUser: 999
fsGroup: 999
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: test-mysql-123
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: mysql.presslabs.org
app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql
app.kubernetes.io/version: 5.7.31
mysql.presslabs.org/cluster: test-mysql-123
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
schedulerName: default-scheduler
volumeClaimTemplates:
- kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: data
creationTimestamp: null
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: mysql.presslabs.org/v1alpha1
kind: MysqlCluster
name: test-mysql-123
uid: 5e877cc3-5167-49da-904e-820940cf1a6d
controller: true
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
limits:
storage: 1Gi
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: local-path
volumeMode: Filesystem
status:
phase: Pending
serviceName: mysql
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
partition: 0
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
status:
observedGeneration: 1
replicas: 1
readyReplicas: 1
currentReplicas: 1
updatedReplicas: 1
currentRevision: test-mysql-123-mysql-6b8f5577c7
updateRevision: test-mysql-123-mysql-6b8f5577c7
collisionCount: 0
availableReplicas: 1