Import a Linux Virtual Machine with Ubuntu from an External Platform¶
This page provides a detailed introduction on how to import Linux virtual machines from the external platform VMware into the virtual machines of AI platform through the command line.
Info
The external virtual platform in this document is VMware vSphere Client, abbreviated as vSphere. Technically, it relies on kubevirt cdi for implementation. Before proceeding, the virtual machine imported on vSphere needs to be shut down. Take a virtual machine of the Ubuntu operating system as an example.
Fetch Basic Information of vSphere Virtual Machine¶
-
vSphere URL: Fetch information on the URL of the target platform
-
vSphere SSL Certificate Thumbprint: Need to be fetched using openssl
Output will be similar to:openssl s_client -connect 10.64.56.11:443 </dev/null | openssl x509 -in /dev/stdin -fingerprint -sha1 -nooutCan't use SSL_get_servername depth=0 CN = vcsa.daocloud.io verify error:num=20:unable to get local issuer certificate verify return:1 depth=0 CN = vcsa.daocloud.io verify error:num=21:unable to verify the first certificate verify return:1 depth=0 CN = vcsa.daocloud.io verify return:1 DONE sha1 Fingerprint=C3:9D:D7:55:6A:43:11:2B:DE:BA:27:EA:3B:C2:13:AF:E4:12:62:4D # Value needed -
vSphere Account: Fetch account information for vSphere, and pay attention to permissions
-
vSphere Password: Fetch password information for vSphere
-
UUID of the virtual machine to be imported: Need to be fetched on the web page of vSphere
-
Access the Vsphere page, go to the details page of the virtual machine to be imported, click Edit Settings , open the browser's developer console at this point, click Network -> Headers , find the URL as shown in the image below.
-
Click Response , locate vmConfigContext -> config , and finally find the target value uuid .
-
-
Path of the vmdk file of the virtual machine to be imported
Network Configuration¶
Different information needs to be configured based on the chosen network mode. If a fixed IP address is required, you should select the Bridge network mode.
- Create a Multus CR of the ovs type. Refer to Creating a Multus CR.
-
Create subnets and IP pools.
apiVersion: spiderpool.spidernet.io/v2beta1 kind: SpiderIPPool metadata: name: test2 spec: ips: - 10.20.3.90 subnet: 10.20.0.0/16 gateway: 10.20.0.1 --- apiVersion: spiderpool.spidernet.io/v2beta1 kind: SpiderIPPool metadata: name: test3 spec: ips: - 10.20.240.1 subnet: 10.20.0.0/16 gateway: 10.20.0.1 --- apiVersion: spiderpool.spidernet.io/v2beta1 kind: SpiderMultusConfig metadata: name: test1 namespace: kube-system spec: cniType: ovs coordinator: detectGateway: false detectIPConflict: false mode: auto tunePodRoutes: true disableIPAM: false enableCoordinator: true ovs: bridge: br-1 ippools: ipv4: - test1 - test2
Fetch vSphere Account Password Secret¶
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: vsphere # Can be changed
labels:
app: containerized-data-importer # Do not change
type: Opaque
data:
accessKeyId: "username-base64"
secretKey: "password-base64"
Write a KubeVirt VM YAML to create VM¶
Tip
If a fixed IP address is required, the YAML configuration differs slightly from the one used for the default network. These differences have been highlighted.
apiVersion: kubevirt.io/v1
kind: VirtualMachine
metadata:
annotations:
kubevirt.io/latest-observed-api-version: v1
kubevirt.io/storage-observed-api-version: v1
virtnest.io/alias-name: ""
virtnest.io/image-secret: ""
creationTimestamp: "2024-05-23T06:46:28Z"
finalizers:
- kubevirt.io/virtualMachineControllerFinalize
generation: 1
labels:
virtnest.io/os-family: Ubuntu
virtnest.io/os-version: "22.04"
name: export-ubuntu
namespace: default
spec:
dataVolumeTemplates:
- metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: export-ubuntu-rootdisk
namespace: default
spec:
pvc:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
storageClassName: local-path
source:
vddk:
backingFile: "[A05-09-ShangPu-Local-DataStore] virtnest-export-ubuntu/virtnest-export-ubuntu.vmdk"
url: "https://10.64.56.21"
uuid: "421d6135-4edb-df80-ee54-8c5b10cc4e78"
thumbprint: "D7:C4:22:E3:6F:69:DA:72:50:81:12:FA:42:18:3F:29:5C:7F:41:CA"
secretRef: "vsphere"
initImageURL: "release.daocloud.io/virtnest/vddk:v8"
runStrategy: Manual
template:
metadata:
annotations:
ipam.spidernet.io/ippools: '[{"cleangateway":false,"ipv4":["test2"]}]' // Add spiderpool network here
creationTimestamp: null
spec:
architecture: amd64
domain:
devices:
disks:
- bootOrder: 1
disk:
bus: virtio
name: rootdisk
interfaces: // Modify the network configuration
- bridge: {}
name: ovs-bridge0
machine:
type: q35
resources:
requests:
memory: 4Gi
networks: // Modify the network configuration
- multus:
default: true
networkName: kube-system/test1
name: ovs-bridge0
volumes:
- dataVolume:
name: export-ubuntu-rootdisk
name: rootdisk
Access VNC to verify successful operation¶
-
Modify the network configuration of the virtual machine
-
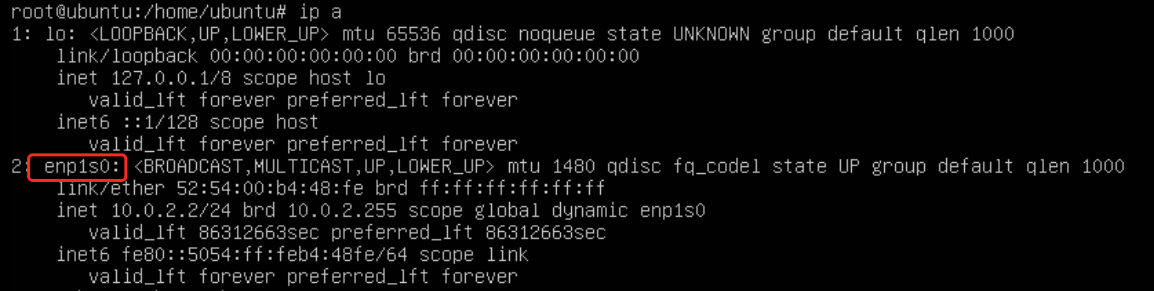
Check the current network
When the actual import is completed, the configuration shown in the image below has been completed. However, it should be noted that the enp1s0 interface does not contain the inet field, so it cannot connect to the external network.
-
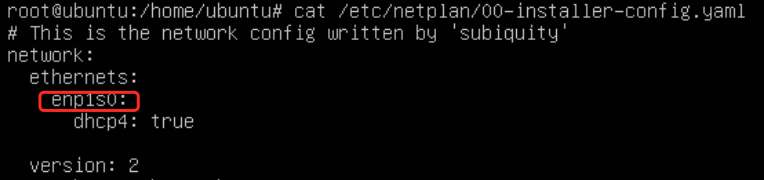
Configure netplan
In the configuration shown in the image above, change the objects in ethernets to enp1s0 and obtain an IP address using DHCP.
-
Apply the netplan configuration to the system network configuration
-
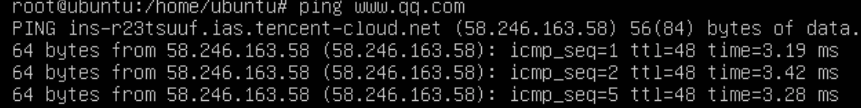
Perform a ping test on the external network
-
Access the virtual machine on the node via SSH.